The former French Cameroon and part of British Cameroon merged in 1961 to form the present country. Cameroon has generally enjoyed stability, which has permitted the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a petroleum industry. Despite slow movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Paul BIYA.
Population
19,294,149
Country comparison to the world: 58
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:Cameroonian(s)
Adjective: Cameroonian
Ethnic groups
Cameroon Highlanders 31%, Equatorial Bantu 19%, Kirdi 11%, Fulani 10%, Northwestern Bantu 8%, Eastern Nigritic 7%, other African 13%, non-African less than 1%
Religions
indigenous beliefs 40%, Christian 40%, Muslim 20%
Languages
24 major African language groups, English (official), French (official)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of Cameroon
Conventional short form:Cameroon
Local long form:Republique du Cameroun/Republic of Cameroon
Local short form:Cameroun/Cameroon
Former:French Cameroon, British Cameroon, Federal Republic of Cameroon, United Republic of Cameroon
Government Type
republic; multiparty presidential regime
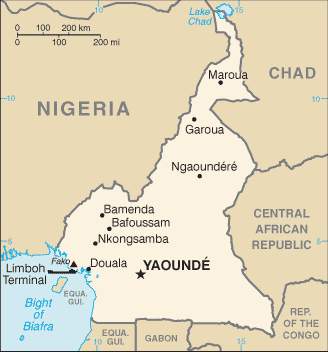
Capital
Name:Yaounde
Geographic coordinates:3 52 N, 11 31 E
Time difference:UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
10 regions (regions, singular - region); Adamaoua, Centre, Est, Extreme-Nord, Littoral, Nord, North-West (Nord-Ouest), Ouest, Sud, South-West (Sud-Ouest)
Independence
1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship)
National Holiday
Republic Day (National Day), 20 May (1972)
Constitution
approved by referendum 20 May 1972; adopted 2 June 1972; revised January 1996
Legal system
based on French civil law system with common law influence; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
20 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Paul BIYA (since 6 November 1982)
Head of government:Prime Minister Philemon YANG (since 30 June 2009)
Cabinet:Cabinet appointed by the president from proposals submitted by the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11 October 2004 (next to be held by October 2011); prime minister appointed by the president
Election results:President Paul BIYA reelected; percent of vote - Paul BIYA 70.9%, John FRU NDI 17.4%, Adamou Ndam NJOYA 4.5%, Garga Haman ADJI 3.7%
Legislative branch
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (180 seats; members are elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms); note - the president can either lengthen or shorten the term of the legislature
Elections:last held on 22 July 2007 (next to be held in 2012)
Election results:percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - CPDM 140, SDF 14, UDC 4, UNDP 4, MP 1, vacant 17
note: the constitution calls for an upper chamber for the legislature, to be called a Senate, but it has yet to be established
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president); High Court of Justice (consists of nine judges and six substitute judges; elected by the National Assembly)
Political Parties and Leaders
Cameroon People's Democratic Movement or CPDM [Paul BIYA]; Cameroonian Democratic Union or UDC [Adamou Ndam NJOYA]; Movement for the Defense of the Republic or MDR [Dakole DAISSALA]; Movement for the Liberation and Development of Cameroon or MLDC [Marcel YONDO]; National Union for Democracy and Progress or UNDP [Maigari BELLO BOUBA]; Progressive Movement or MP; Social Democratic Front or SDF [John FRU NDI]; Union of Peoples of Cameroon or UPC [Augustin Frederic KODOCK]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Human Rights Defense Group [Albert MUKONG, president]; Southern Cameroon National Council [Ayamba Ette OTUN]
International organization participation
ACCT, ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, C, CEMAC, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Joseph FOE-ATANGANA
Chancery: 2349 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 265-8790
FAX: [1] (202) 387-3826
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Janet E. GARVEY
Embassy:Avenue Rosa Parks, Yaounde
Mailing address: P. O. Box 817, Yaounde; pouch: American Embassy, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-2520
Telephone:[237] 2220 15 00; Consular: [237] 2220 16 03
FAX:[237] 2220 16 00 Ext. 4531; Consular FAX: [237] 2220 17 52
branch office(s): Douala
Flag description
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), red, and yellow, with a yellow five-pointed star centered in the red band; the vertical tricolor recalls the flag of France; red symbolizes unity, yellow the sun, happiness, and the savannahs in the north, and green hope and the forests in the south; the star is referred to as the "star of unity"
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia